Operators
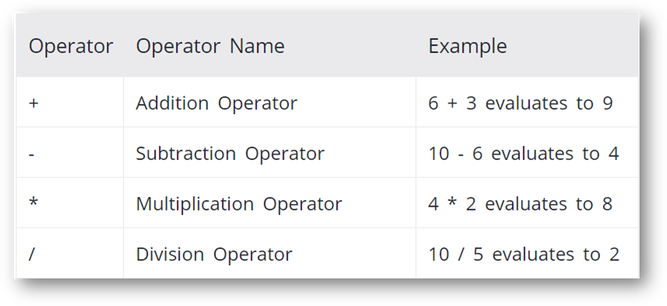
Basic Operators
Here is a list of the basic mathematical calculations which can be performed.
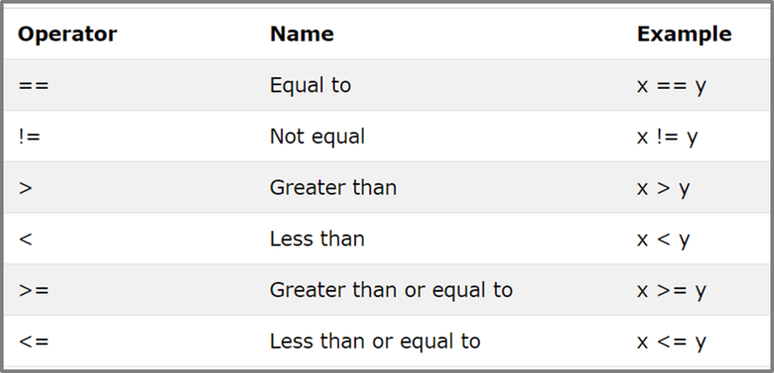
Operators to use for Comparison
Use the table below to compare two variables.
For example to check if the value stored in variable FirstNum is lower than the value stored in variable SecondNum use the following code:
if (FirstNum < SecondNum)
{
// do something
}
The Invisible True
Note if you do not use a comparison symbol, you are checking if the value is true. So the code here..
bool IsFinished = true;
if (IsFinished == true)
{
// do something
}
...is the same as the code here where == true has been ommitted.
bool IsFinished = true;
if (IsFinished)
{
// do something
}
Logical operators
The following logical operators allow you to test more than one comparison.

Example: Using Logical and
For example to check if both NumOne and NumTwo are greater than NumThree use the following code:
if ((NumOne> NumThree) && (NumTwo > NumThree))
{
// do something
}
Note: You will need to put round brackets are each separate test and then both tests.
Finding the Exponential
Exponential uses powers represented in Maths with the symbol ^.
Two to the power of two would be represented mathematically as:
2^2
Which is the same as:
2*2
Two to the power of three would be be represented mathematically as:
2^3
which is the same as:
2*2*2
The Exponential function
Use the Math.Pow function to find the exponential. Here is the code to store in result 2 to the power of 3:
double result = Math.Pow(2, 3);
The Random Function
The code below finds a random number between 0 and 200. Note you only need the first line once. Use rnd.Next() every time you want a random number.
Random rnd = new Random();
int result = rnd.Next(0, 200);